We do an organic bed with our own hands: general principles of arrangement, types of smart beds
 Organic beds, smart beds, warm beds - as soon as they do not name special designs that help ease the hard work of farmers and get a good harvest even in a limited area of the site. All three names fully reflect the essence of such agriculture: vegetables are grown not in the soil in the garden, but directly on organic fertilizers, which provide plants with nutrition, and also release heat during decomposition, heating the garden and protecting the plantings from frost. In addition, the territory for planting is presented in the form of a long and narrow strip-bed (most often with a restriction around the perimeter) - it is much easier to look after it than to run around the whole garden with a hoe or a hose.
Organic beds, smart beds, warm beds - as soon as they do not name special designs that help ease the hard work of farmers and get a good harvest even in a limited area of the site. All three names fully reflect the essence of such agriculture: vegetables are grown not in the soil in the garden, but directly on organic fertilizers, which provide plants with nutrition, and also release heat during decomposition, heating the garden and protecting the plantings from frost. In addition, the territory for planting is presented in the form of a long and narrow strip-bed (most often with a restriction around the perimeter) - it is much easier to look after it than to run around the whole garden with a hoe or a hose.
General principles for the construction of smart beds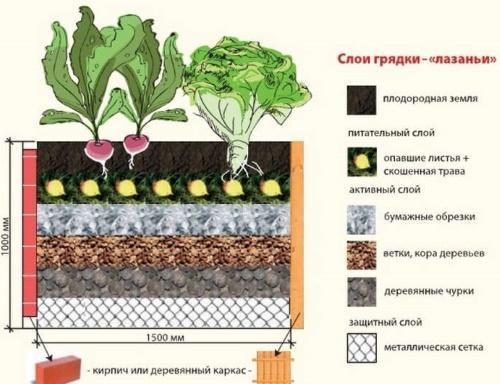
Even a novice gardener can make an organic garden with his own hands. The main thing in this business is to properly prepare the soil and lay the "organic layer cake" on which crops will grow, namely:
- For the bottom layer, you need to use coarse or brown organic matter that decomposes for a long time (branches, wood chips, corn and sunflower trunks).
- The second layer is made of green organic matter that quickly decays (leaves, grass, kitchen waste from fruits and vegetables).
- Lay humus and ash in a third layer.
- Top the garden bed ready compost or fertile soil and mulch with straw.
Since organic matter serves as the main material for a warm bed, it is better to start laying in the fall, when it is abundant. If there is a compost heap, the garden bed can be made in the spring, but then after all layers have been laid, it is necessary to spill it with warm water and cover it with a film for a while to start a "thermal reaction".
Equally important is the arrangement of row spacings for the maintenance of the beds: they are usually mulched with mown grass or covered with cardboard or film and also covered from above so that weeds do not grow.
The shape of a smart bed depends on the desire of the summer resident, but most often they use two types:
- high beds;
- trenches.
How to make tall beds?
High beds assume that the plants will be grown above soil level. To do this, you need to make a box, container or just a tall frame, place them in a well-lit place and fill with organic "puff cake". Stationary smart beds can be immediately laid out of stones, raising them to the desired height, while the width is usually about 60 cm. It is very convenient to care for a high bed, moreover, it keeps heat well, but you will have to water more often.
Tall beds are ideal for areas that are frequently heated.
How to make a smart trench bed?
In contrast to tall beds, trenches should be constructed so that crops grow at or near soil level. To do this, at the chosen place, dig a ditch about 0.5 m deep and fill it with organic matter according to the generally accepted scheme. If desired, sides can be made around the perimeter.
In-depth organic beds are a good option for areas that dry out quickly: they retain moisture for a long time, especially with additional mulching.