Foundation depth: audit of the significance of influencing factors
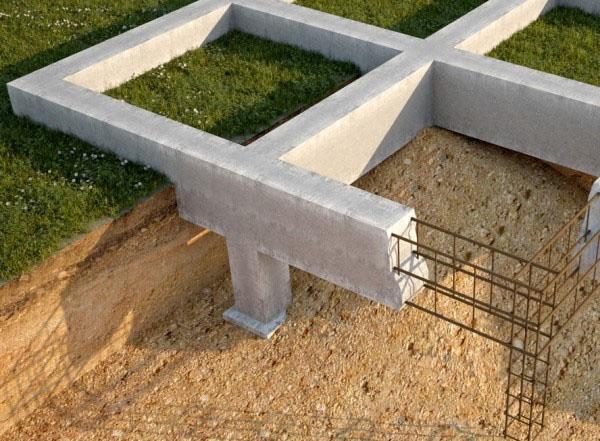 When laying the foundation of a building, the type and number of storeys of the house, its weight, features of the terrain, all characteristics of the soil are taken into account. These factors determine the type and depth of the foundation. The latter parameter is calculated according to SNiP 2.02.01-83 Foundations of buildings and structures.
When laying the foundation of a building, the type and number of storeys of the house, its weight, features of the terrain, all characteristics of the soil are taken into account. These factors determine the type and depth of the foundation. The latter parameter is calculated according to SNiP 2.02.01-83 Foundations of buildings and structures.
Foundation classification by depth
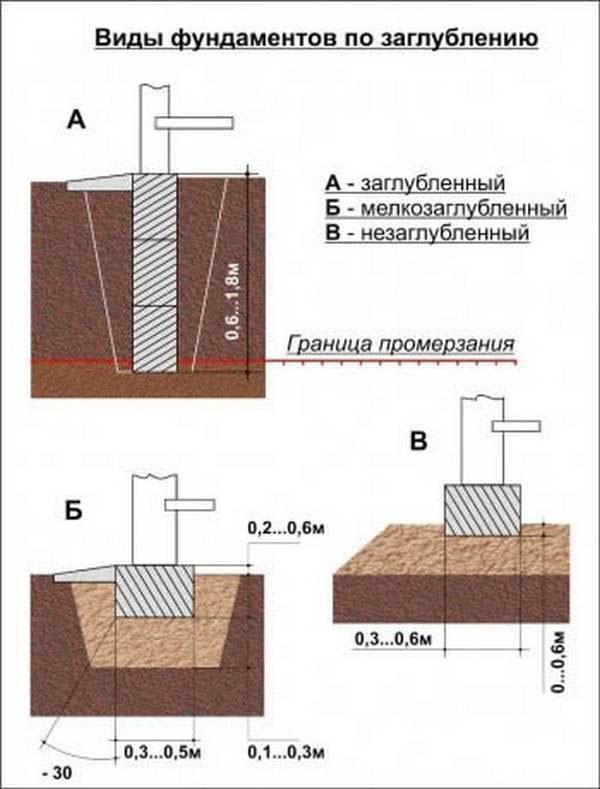
In the regulatory building base, the foundations, depending on the depth, are divided into three types:
- Recessed. Provides a solid foundation for heavy buildings on all types of soil.
- Shallow. The depth of the shallow foundation does not reach the place where the soil is already frozen. They are used on solid soils, with a high level of groundwater, in the construction of structures that do not have basements and basements.
- Shallow. They are used in the construction of light structures on heaving and soils with increased heaving, soils with weak subsidence, as well as in the construction of heavy buildings on rocky soils.
Factors that determine how deep the foundation should be:
- elevation and general groundwater level;
- characteristics of the local climate, indicators of hydrogeological surveys;
- place of organization of the construction site;
- the structure of the building, the nature of the loads exerted on the base.
If there are other structures next to the house under construction, when calculating the depth of the foundation, I take into account the technical characteristics of their foundation.
The value of soil water saturation
 There is a general rule: the foundation is laid so that the maximum level of groundwater rise is below the base. Then the terms and cost of construction are significantly reduced.
There is a general rule: the foundation is laid so that the maximum level of groundwater rise is below the base. Then the terms and cost of construction are significantly reduced.
The depth of the foundation, depending on the geological characteristics, is determined by two factors:
- The presence of moisture in the soil.
- Groundwater level and its influence on frost heave of soil in the region.
The strip foundation is poured at a height of at least 0.5 m higher than the groundwater runs.
With high soil moisture, the foundation material will get wet and from this will gradually collapse. If we take into account that the main material for the formation of foundations is concrete, then the destructive effect of moisture in low frosts increases several times.
Taking into account the concentration of moisture in the design differs depending on the type of base under the building foundation:
- Rocky, sandy soils of large and medium fractions, gravelly, coarse-grained, having sand as a filler. They are not limited to the depth of the foundation in terms of the water table.
- A foundation in clay, loam, in a soil consisting of large fragments filled with dusty-clay fractions is always designed below the level of soil freezing, regardless of the level at which the groundwater is located.
- For fine sand and silty soil, the location of the groundwater in relation to the level of soil freezing is important. If the waters pass at a level of 2 meters down from freezing, then it does not matter what the depth of the foundation should be.
How the climate affects the calculation of the depth of the foundation
 The climatic conditions of the region where construction work is taking place affect the depth of soil freezing. With a certain degree of approximation, this value can be determined from the maps "Boundaries of soil freezing depths".More accurate calculations can be made in relation to a narrow building site.
The climatic conditions of the region where construction work is taking place affect the depth of soil freezing. With a certain degree of approximation, this value can be determined from the maps "Boundaries of soil freezing depths".More accurate calculations can be made in relation to a narrow building site.
Calculation of the standard indicator
For an area where the soil freezes by more than 2.5 m, the standard index of the freezing depth is calculated using the formula:
where Mt - the summed number of absolute average monthly negative temperatures for a given region, d0 - coefficient depending on the type of soil.
To calculate Mt the data is taken from the statistics service. Coefficient d0 equal to 0.34 for coarse soils, for loam and clay - 0.23, for coarse, medium and gravelly sands - 0.3, for fine sandy and dusty soils - 0.28.
How to take into account the heat transfer of a building
To determine the depth of freezing of a structure in real conditions, use the formula:
In this expression, the coefficient kh is taken taking into account two factors:
- The building is heated and the ground will be additionally warmed up, so kh will be downward. It is taken in special tables, where the gradation is based on the presence of a basement, basement floor and the average daily air temperature in rooms that are adjacent to the foundation.
- In the absence of heating. In this case, kh - safety factor equal to 1.1 for all types of buildings.
We study the features of soils
 Before calculating the depth of the foundation, the type of soil is determined. This service can be ordered from specialists or performed independently.
Before calculating the depth of the foundation, the type of soil is determined. This service can be ordered from specialists or performed independently.
On a fertile soil layer, no foundations are poured. It is completely removed.
Under the fertile layer there is one or more layers suitable for soil construction:
- Rocky soil that does not require deepening of the strip and monolithic foundation. It does not swell in winter, moisture does not accumulate in it, it is not subject to settling.
- Gravel, stones, crushed stone, coarse sand create a reliable foundation, on which the depth of the foundation is from 0.5 m.
- Clay soil freezes to a level of 0.5-1 m, is mobile when wet, has uneven shrinkage. But if there is not a lot of precipitation in the region, and the groundwater is very deep, the foundation is laid at a depth of at least 0.75 m.
- Fine-grained sand has increased mobility and loses its stability with strong moisture. With deep groundwater, it is recommended to deepen to a more stable base. The freezing depth of sandy soil, in which there are clay particles, is from 0.6 to 2 m.
- Unreliable soil type peat is used for construction on columnar foundations.

When determining the type of soil yourself, consider the following:
- the clay is dense, it is difficult to dig it, it does not crumble when rolled into a roller;
- sandy loam will consist of sand with clay fractions, and the rolled flagellum will crumble;
- loam is based on clay and inclusions of sand (any figurine from such a mixture will break).
Knowing the type of soil already allows you to move on to determining the type of foundation and the depth of its laying.
Features of the building and the depth of the foundation
The first thing to consider is the weight of the entire structure. Buildings with a higher mass require a deeper foundation. The bearing capacity of the soil is also taken into account.
When building a frame one-story building on heaving soils, the foundation is deepened by 0.5 m, and for a 2-3-story timber houses this figure will be at least 1.5 m. When replacing the timber with a brick, the depth of the foundation will also increase.
To take into account the bearing capacity of the soil, calculate the weight of the entire building, foundation, communications and internal equipment per unit area. If the standard indicator does not correspond to the calculated one, the parameters of the foundation are changed.
When designing a foundation, the structural features of the structure and its location are taken into account:
- the foundation is located below the basement floor by at least 0.4 m;
- the level of the foundation is aligned with the foundation of all buildings in close contact with the structure being erected;
- it is advisable to bypass the main communications with construction, but if this does not work, then the foundation is laid under the pipes.
Depth of belt support
 The tape-type foundation is easy to install and design, suitable for most types of building structures. Recommended for use on soil with mild heaving, not recommended where soil water saturation is high.
The tape-type foundation is easy to install and design, suitable for most types of building structures. Recommended for use on soil with mild heaving, not recommended where soil water saturation is high.
The depth of the strip foundation is determined by the parameters:
- the level of soil freezing;
- height of groundwater flow;
- the severity of the heaving of the soil.
The combination of these factors leads to the fact that the heaving of the soil will increase with an increase in the depth of freezing of the soil and the proximity of groundwater. Such soil will squeeze the foundation from below and push it up. The deep location of the foundation reduces the intensity of such processes.
The standards determine the minimum penetration rates:
- 0.45 m in low-loamy soils;
- 0 m on rocky ground;
- 0.75 m in heaving soils;
- at the level of occurrence of stable soil with water-saturated and moving upper soil layers.
The maximum burial depth is 2.5 m for all types of soil.
In order not to decide what the depth of the foundation depends on, it is possible to equip the thermal insulation of the soil and insulation of the foundation, mount drainage and groundwater drainage system.
Other types of foundation
 The columnar base is used for light buildings. Such a foundation is effective where the soil freezes heavily. It is lowered into the ground below the freezing point by 10-25 cm.
The columnar base is used for light buildings. Such a foundation is effective where the soil freezes heavily. It is lowered into the ground below the freezing point by 10-25 cm.
To lay piles and select their type, soil properties are determined. Such a base is made mainly of concrete. Deep pile foundations are lowered to a depth of 1 m or more, which depends on the bearing capacity of the structure.
The most stable option for the base of the building is slab or solid. Formed from reinforced concrete slabs. It is buried down to 50 cm in any soil.
Determining the depth for laying a foundation is a complex task that must be solved even at the stage of designing a building structure.