The leading factor in the fertility of different soil types is humus
 Fertility and humus are closely related concepts. From the Latin language, this term is translated as soil or earth. Although today farmers grow crops on hydroponics or artificial soil without any problems, this component of fertility is indispensable. To increase the yield percentage, first you need to find out what soil humus is, and then consider the process of its formation.
Fertility and humus are closely related concepts. From the Latin language, this term is translated as soil or earth. Although today farmers grow crops on hydroponics or artificial soil without any problems, this component of fertility is indispensable. To increase the yield percentage, first you need to find out what soil humus is, and then consider the process of its formation.
Humus is ...

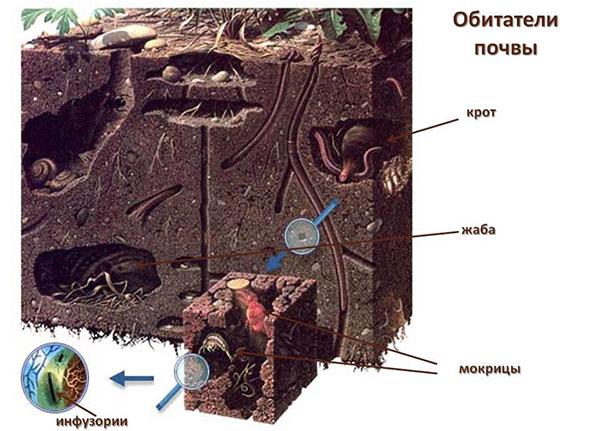 So how is humus formed? Complex biochemical processes occur in the upper soil layer - decomposition of organic remains without oxygen. They cannot happen without participation:
So how is humus formed? Complex biochemical processes occur in the upper soil layer - decomposition of organic remains without oxygen. They cannot happen without participation:
- animals;
- soil microorganisms;
- plants.
Dying away, they leave behind a significant trace in soil formation. The decomposed waste products of these organisms also accumulate here. In turn, such organic substances are resistant to microbes, which allows them to accumulate in the soil horizon.
 This biomass serves as a real depot for all higher organisms. The components contained in it saturate the roots of plants with energy, and also nourish them with all the necessary elements:
This biomass serves as a real depot for all higher organisms. The components contained in it saturate the roots of plants with energy, and also nourish them with all the necessary elements:
- humin;
- humic acids;
- humic compounds.
The thickness of such a cover can reach (in the temperate latitudes of the planet) up to 1.5 meters. In some territories it is 10-16% of the land, while in others it is only 1.5%. At the same time, peatlands contain about 90% of these organic formations.
 The formation of humus directly depends on the mineralization process - the decomposition of biomass (under the influence of oxygen) into simple mineral and organic compounds. Under normal natural conditions, this happens evenly, without damage to humification.
The formation of humus directly depends on the mineralization process - the decomposition of biomass (under the influence of oxygen) into simple mineral and organic compounds. Under normal natural conditions, this happens evenly, without damage to humification.
Composition
 Before paying attention to the beneficial properties of this soil cover, you need to consider its composition. The highest concentration of useful elements is contained exclusively in the upper part of the horizon. With deepening, they become smaller, since all "participants" in this process live at a level of 50-70 cm from the surface. Therefore, the formation of fertile layers is impossible without:
Before paying attention to the beneficial properties of this soil cover, you need to consider its composition. The highest concentration of useful elements is contained exclusively in the upper part of the horizon. With deepening, they become smaller, since all "participants" in this process live at a level of 50-70 cm from the surface. Therefore, the formation of fertile layers is impossible without:
- certain types of mushrooms;
- earthworms;
- bacteria.
 The processing of organic components, as well as the excrement of invertebrates, leads to the formation of priceless humus. It is the worms that are decisive in its formation. It should be noted that about 450-500 individuals live in 1 m² of humus. Each of them eats up plant debris and bacteria. The organics deposited by them make up a large percentage of the nutrient biomass. The composition of humus includes the following chemical elements (the percentage depends on the type of soil):
The processing of organic components, as well as the excrement of invertebrates, leads to the formation of priceless humus. It is the worms that are decisive in its formation. It should be noted that about 450-500 individuals live in 1 m² of humus. Each of them eats up plant debris and bacteria. The organics deposited by them make up a large percentage of the nutrient biomass. The composition of humus includes the following chemical elements (the percentage depends on the type of soil):
- Fulvic acids (30 - 50%). Nitrogen-containing soluble (high molecular weight) organic acids. They lead to the formation of compounds that destroy mineral formations.
- Humins (15 - 50%). This includes elements that have not completed the humification process. Moreover, their livelihoods depend on minerals.
- Wax resins (2 to 6%).
- Humic acids (7 - 89%). They are insoluble, although under the influence of alkalis they can decompose into individual elements. Each of them contains one of the leading components: nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen and carbon. When acids come in contact with other components, salts can form in the soil.
- Insoluble residue (19 - 35%). This applies to various saccharides, enzymes, alcohols and other elements.
 The table of humus content in the main groups of soils shows the amount of nitrogen and carbon for every 100 or 20 cm of soil. The measurement is carried out in t / ha. This is the general picture of the stocks of fertile lands in Russia.
The table of humus content in the main groups of soils shows the amount of nitrogen and carbon for every 100 or 20 cm of soil. The measurement is carried out in t / ha. This is the general picture of the stocks of fertile lands in Russia.
If fertilizers are applied too often and in huge quantities (mineral, in particular, nitrogen), then this will lead to rapid decomposition of the biomass. In the first years, the yield, of course, will increase several times. But over time, the volume of the fertile layer will significantly decrease, and the yield will deteriorate.
Beneficial features
In agriculture, the most important thing is the preservation of this organic horizon. Over the past half century, due to erosion on the territory of Russia, as well as Ukraine, the top cover has decreased by almost half. Exposure to wind and water caused the rich soil layers to be blown away / washed away. The content of humus in the soil is considered by ecologists and agrarians to be both a factor of fertility and the main criterion for buying land. After all, it is he who is responsible for the quality characteristics of the soil, and for the following reasons:
- It contains an abundance of nutrients that are needed for the productive life of plants. This is almost 99% of the nitrogen found in nature, as well as over 60% of all phosphorus.

- Contributes to the saturation of the earth with oxygen, making it looser. Thanks to this, the root systems of crops and microorganisms living in the soil receive a sufficient portion of air.

- Forms the structure of the soil. As a result, clay and sand do not accumulate. Organic compounds stick together mineral particles into lumps, forming a kind of lattice. Moisture passes through it, which is retained in the formed voids. This is how the vegetation receives water. Also, the porous structure protects the earth from sudden changes in temperature and erosion anomalies.

- Humus promotes uniform heating of the soil. Complex biochemical processes take place in this layer. The result of such reactions is the release of heat. As noted above, fertile soil has a darker shade. Brown-black tones are the best at attracting and absorbing ultraviolet rays.
Organic compounds protect the land from the harmful effects of harsh chemicals generated by human activities. These elements "preserve" resinous carbons, salts, metals and radionuclides, leaving them forever in the bowels of the earth and preventing plants from assimilating them.
 The only problem for all farmers is the natural zone of growing crops, as well as the types of soils in which the humus content (the table is given in the article) is strikingly different. Therefore, in order to increase the fertility of your lands, you need to determine the level of biomass in them, taking as a basis the natural conditions of the region.
The only problem for all farmers is the natural zone of growing crops, as well as the types of soils in which the humus content (the table is given in the article) is strikingly different. Therefore, in order to increase the fertility of your lands, you need to determine the level of biomass in them, taking as a basis the natural conditions of the region.
Humus stock map
 In areas with a very harsh climate, the process of soil formation is catastrophically slow. Due to the weak heating of the upper layer, plants and microorganisms are deprived of favorable conditions for a full-fledged existence.
In areas with a very harsh climate, the process of soil formation is catastrophically slow. Due to the weak heating of the upper layer, plants and microorganisms are deprived of favorable conditions for a full-fledged existence.
Tundra
 Here you can see huge areas of conifers and shrubs. The slopes are mostly covered with moss. In the tundra, the humus content is 73-80 t / ha in a one-meter layer. These areas are so wet that it leads to the accumulation of clayey rocks. As a result, tundra soils have the following structure:
Here you can see huge areas of conifers and shrubs. The slopes are mostly covered with moss. In the tundra, the humus content is 73-80 t / ha in a one-meter layer. These areas are so wet that it leads to the accumulation of clayey rocks. As a result, tundra soils have the following structure:
- top cover - litter, consisting of undecomposed plant remains;
- humus layer, which is very weakly expressed;
- helium layer (comes with a bluish tint);
- eternal Frost.
Oxygen hardly penetrates into such soils. The presence of air is essential for the microbiological activity of organisms. Without it, they die or freeze.
Taiga
 Broad-leaved trees are found in this area. They form dense mixed forests. In the steppe zones, not only moss grows, but also herbal plants. Spring (often thawed snow) and autumn rainy seasons over-wet the soil. Such flows wash away the reserves of the humus horizon.
Broad-leaved trees are found in this area. They form dense mixed forests. In the steppe zones, not only moss grows, but also herbal plants. Spring (often thawed snow) and autumn rainy seasons over-wet the soil. Such flows wash away the reserves of the humus horizon.
Here it is formed and lies under the forest floor. Many sources provide different indicators of the humus content in the taiga. For the following types of soils, they are as follows (per 1 m², t / ha):
- podzol (strong, medium and weak) - from 50 to 120;
- gray forest - 76 or 84;
- sod-podzolic - no more than 128, and no less than 74;
- taiga-permafrost contain a very low percentage.
To grow crops on land like this beds should be fertilized regularly with quality substances. Only in this case can a high yield be achieved.
Chernozem
 All known varieties of chernozem are considered the leader and favorite in this fertility rating. Organic humus in them reaches a depth of 80 cm or 1.2 meters. They can rightfully be called the most fertile lands. It is a favorable soil for the growth of cereals (wheat), sugar beets, corn or sunflowers. From the following list, you can see the variation in humus content in different types of chernozem (t / ha, per 100 cm):
All known varieties of chernozem are considered the leader and favorite in this fertility rating. Organic humus in them reaches a depth of 80 cm or 1.2 meters. They can rightfully be called the most fertile lands. It is a favorable soil for the growth of cereals (wheat), sugar beets, corn or sunflowers. From the following list, you can see the variation in humus content in different types of chernozem (t / ha, per 100 cm):
- typical (500-600);
- greeted (up to 400);
- leached (within 550);
- powerful (over 800);
- southern West Caucasian (390);
- degraded (up to 512).
 It should be understood that the indicators for virgin, arable and developed types of land are different. To familiarize yourself with the composition of each of these groups, a table is given. In steppe and arid areas, chestnut soils are widespread, which contain no more than 100-230 t / ha of humus. For desert (brown and gray types of soil cover) regions, this figure is about 70 t / ha. As a result, farmers constantly have to deal with the salinization of fields.
It should be understood that the indicators for virgin, arable and developed types of land are different. To familiarize yourself with the composition of each of these groups, a table is given. In steppe and arid areas, chestnut soils are widespread, which contain no more than 100-230 t / ha of humus. For desert (brown and gray types of soil cover) regions, this figure is about 70 t / ha. As a result, farmers constantly have to deal with the salinization of fields.
Drought is the main enemy of these types of land. Therefore, plantations may need abundant irrigation.
Ways to increase yields
By understanding how the organic layer of the earth is formed, the gardener will be able to increase the humus content in podzolic soils, which suffer from excess moisture. In the struggle for the fertility of such zones, the following actions are applied:
- fertilize the garden with manure, peat or humus;
- use / create compost;

- constantly loosen the earth so that oxygen flows to the roots and earthworms;
- take care of a sufficient number of soil bacteria, you can use special biological products or scatter weeds around the garden, and organic.

Waste of plant origin can be buried in your beds, thereby taking care of the nutrition of ground inhabitants.
Such measures of looking after their land holdings will help the farmer to keep the soil "alive".  At the same time, the yield will increase several times.
At the same time, the yield will increase several times.