How to organize the storage of vegetables in piles and trenches to save the harvest until spring
 The harvested crop is usually stored in equipped subfloors, basements or cellars. In the absence of these, many farmers and gardeners use storing vegetables in piles and trenches - the "old-fashioned" method, which is simple and allows you to preserve the harvest without losing taste and marketability.
The harvested crop is usually stored in equipped subfloors, basements or cellars. In the absence of these, many farmers and gardeners use storing vegetables in piles and trenches - the "old-fashioned" method, which is simple and allows you to preserve the harvest without losing taste and marketability.
What is a pile and a trench
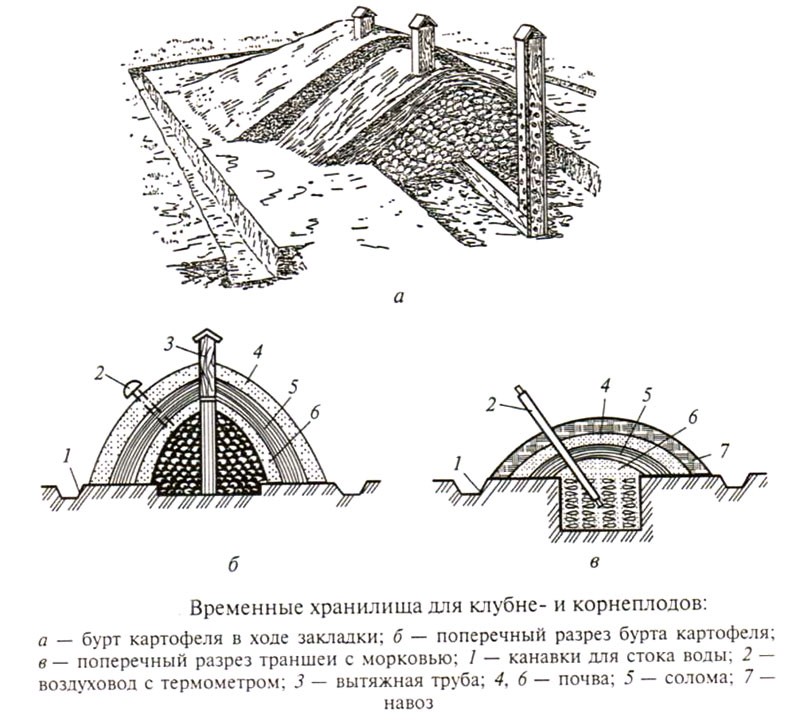
Burt is an elongated embankment, inclined on both sides and covered from above with soil, straw or other insulating material. This is the simplest and most common way to store potatoes, cabbage and root vegetables. Burts can be ground and semi-ground. In the first case, vegetables are poured onto a flat surface, in the second, they are poured into special pits.
 The storage of vegetables in the ground is also carried out using trenches. In this case, the harvested crop is laid in an elongated, oblong trench, which is then insulated and covered with a protective material from moisture. The main difference between a trench and a pile is that vegetables are stored below the ground level, in the pile - above it.
The storage of vegetables in the ground is also carried out using trenches. In this case, the harvested crop is laid in an elongated, oblong trench, which is then insulated and covered with a protective material from moisture. The main difference between a trench and a pile is that vegetables are stored below the ground level, in the pile - above it.
When choosing the best way to store vegetables in piles and trenches, you need to take into account the climatic features of a particular region. For southern regions with warm winters, piles are more suitable; in northern regions with severe frosts, it is better to use trenches.
Choosing the right place
 For storing vegetables in piles and trenches, it is necessary to choose the right place for placing the storage. The best option would be a dry and elevated area with a low groundwater level - at least 1.8-2 m from the ground surface.
For storing vegetables in piles and trenches, it is necessary to choose the right place for placing the storage. The best option would be a dry and elevated area with a low groundwater level - at least 1.8-2 m from the ground surface.
 It is best to equip a vegetable storage in an area with a slight slope - in this case, storm water will quickly drain and not accumulate near a pile or trench.
It is best to equip a vegetable storage in an area with a slight slope - in this case, storm water will quickly drain and not accumulate near a pile or trench.
Storage facilities should be located along the slope.
Despite the fact that the pile and the trench are additionally covered with covering material, it is advisable to choose an area that is protected from drafts. Many gardeners arrange piles in length from north to south. In this way, its sides will be sheltered from the north winds.
Pile and trench sizes

Before you make a storage for vegetables, you need to decide on its size. It is believed that the colder the area, the larger the piles or trenches should be:
- Burt - the optimal width for the southern regions is 1.2-1.4 m, for the central regions of Russia 1.8-2 m. The length of the vegetable embankment is 8-11 m, the height is up to 1.4-1.5 m.
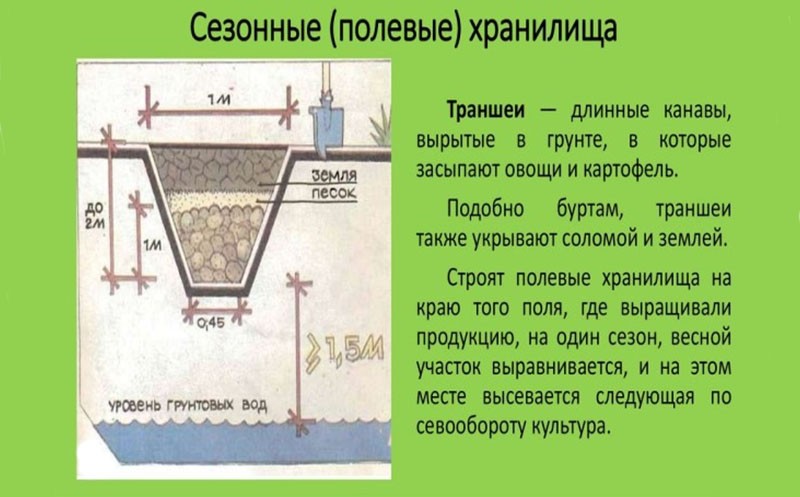
- Trench - in the southern regions, its elongation is 8-10 m, depth is up to 60 cm, width is 70-100 cm.For the central regions of Russia, the parameters increase slightly - length up to 9-12 m, width, depth up to 90-100 cm.
For Siberia, it is best to build a storage facility for large potatoes - up to 1.8-2 m in width and up to 1.4-1.6 m in depth.
Storing vegetables in piles and trenches begins with a bookmark
 Ground piles are laid directly on the ground surface. Before making a semi-terrestrial type shelter, you need to dig a small pit up to 18-20 cm deep. In such a pit, the laid vegetables tolerate the winter much better, as they are protected from sudden temperature changes.
Ground piles are laid directly on the ground surface. Before making a semi-terrestrial type shelter, you need to dig a small pit up to 18-20 cm deep. In such a pit, the laid vegetables tolerate the winter much better, as they are protected from sudden temperature changes.
Basic rules for laying a crop:
- For storage in piles and trenches, only high-quality fruits are used without traces of rot, spoiled fruits will not survive until spring.
- Straw or slightly moistened sand should be poured into the bottom of the pit or trench.
- Additionally, you can use spruce or pine branches - they prevent the development of rot and scare away rodents.
- In the absence of a special ventilation it is advisable to sprinkle vegetables with well-moistened sand - its layer should be at least 1-3 cm thick.
Sand in the trench is used to absorb excess moisture and heat. And also to prevent decay of root crops and the spread of infections in the vegetable store.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the moisture content of the sand. Too dry will draw moisture out of the vegetables, causing them to become lethargic and wilted. You can take it in the palm of your hand. The sand should not crumble into grains, but drops of moisture should also not stand out.
Vegetable storage shelter
 Vegetables are poured in a stack along the entire length of the pile. The top layer of root crops must be covered with straw. But it should not be sprinkled directly on vegetables, as this will cause them to quickly wilt. First of all, potatoes, beets, carrots and white cabbage should be sprinkled with a layer of soil or sand 4-6 cm thick.
Vegetables are poured in a stack along the entire length of the pile. The top layer of root crops must be covered with straw. But it should not be sprinkled directly on vegetables, as this will cause them to quickly wilt. First of all, potatoes, beets, carrots and white cabbage should be sprinkled with a layer of soil or sand 4-6 cm thick.
 Covering the crop with straw is done in two steps. The first layer helps the fruit cool down gradually, so it should be thin enough. The second layer should be poured only when the air temperature drops to about -3 ° C. Root crops should not be covered too early, in which case they will not have time to cool down. But you can't hesitate - in this case, they will quickly freeze.
Covering the crop with straw is done in two steps. The first layer helps the fruit cool down gradually, so it should be thin enough. The second layer should be poured only when the air temperature drops to about -3 ° C. Root crops should not be covered too early, in which case they will not have time to cool down. But you can't hesitate - in this case, they will quickly freeze.
Harvest Shelter Options:
- Straw and soil in layers of 50 cm for potato tubers and 30 cm for cabbage heads.
- The first layer of soil 50 cm thick (for heads of cabbage 30 cm), on top is a layer of sawdust.
- The first layer of soil is 45 cm, then a layer of straw is 30 cm and the same layer of soil.
When sheltering a vegetable store, it is necessary to take into account the climatic features of the region. For southern areas, the layer of covering material should be 5-8 cm thinner. For the Siberian regions and the Urals - 18-20 cm thicker.
The straw for pile and trench cover must be completely dry. Keeping it moist will not only protect the vegetables from freezing. At the same time, it will increase the level of moisture inside the vegetable store.
Pile ventilation methods
 When arranging ventilation in a pile or trench, vegetables are stored much longer without losing marketability and taste. One of the simplest and most common ways is to arrange the supply channel. It helps the penetration of fresh air into the vegetable store and the removal of moist and warm air from it.
When arranging ventilation in a pile or trench, vegetables are stored much longer without losing marketability and taste. One of the simplest and most common ways is to arrange the supply channel. It helps the penetration of fresh air into the vegetable store and the removal of moist and warm air from it.
How to make a supply channel:
- Dig a ditch on the surface of the ground (for the pile) or at the bottom of the trench. It should run along its center along the base and go beyond its boundaries.
- The depth and width of the groove for potato tubers and root crops should be 25-30 cm, for cabbage heads at least 35-45 cm.
- Cover the dug ditch with a wooden trellis on top, otherwise the crop will fall inside.
- Install vertical pipes at the ends of the duct for the penetration of fresh air. Cover their outer openings with visors to protect them from precipitation.
- The design can be improved using plastic pipes, building an exhaust duct from them.
- Install the plastic pipe with a diameter of 15-20 cm in an upright position. Its lower end should be above the crop. And the top one goes through the shelter and rise above it by about 50 cm.
- Place such plastic exhaust ducts at least 3-4 m apart. Also cover the upper holes from precipitation with visors.
Placing vegetables in piles and trenches is a simple and common way to preserve crops until spring without losing their taste and health benefits.Such vegetable stores can be quickly and inexpensively built in a summer cottage.