Features of growing winter wheat
 Winter wheat is a grain crop that is prized for its high yields and unpretentiousness. Its grain is used for the manufacture of cereals, pasta and baked goods, and wheat bran is used as feed for farm animals. The straw from this variety is also of great nutritional value. It is also added to the paper and animal litter industry.
Winter wheat is a grain crop that is prized for its high yields and unpretentiousness. Its grain is used for the manufacture of cereals, pasta and baked goods, and wheat bran is used as feed for farm animals. The straw from this variety is also of great nutritional value. It is also added to the paper and animal litter industry.
Characteristics of culture and stages of its development
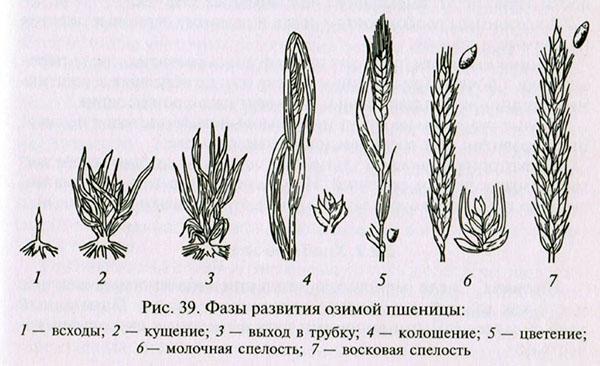
- Shoot is the germination of seeds that occurs after sowing. The total period of the period is from 15 to 25, then the plants enter winter. Ate to plant them late, seedlings continue in the spring after warming.
- Tillering is the process of forming lateral shoots on the stems and roots. The bushiness of plants can be affected by the number of seeds that have been sown in the ground, as well as the depth of their setting.
- Tube emergence is the period that begins when the first node appears on the main stem. The process takes place in the spring, about a month after the resumption of the growing season.
- Heading - the appearance of spikelets on the shoots.
- Flowering begins 4-5 days after spikelets appear and lasts about a week. In a separate ear, flowers appear first on the lower part, and then on the lateral and upper ones.
- Ripening is a long stage in which the grains form in the spikelets and gradually lose moisture. Grains of milky ripeness (40-60% moisture) appear in 2 weeks. Then comes the wax phase of ripeness, the percentage of water in the grains is from 20 to 40%. Full ripeness is the stage when the grain is 15-20% water and becomes hard.
 The growing season of winter wheat can be from 275 to 350 days, including winter. This period depends on the time of planting seeds in the ground and climatic conditions. In spring, the processes resume when the temperature reaches 5 ° C.
The growing season of winter wheat can be from 275 to 350 days, including winter. This period depends on the time of planting seeds in the ground and climatic conditions. In spring, the processes resume when the temperature reaches 5 ° C.
Planting and care technology
 Winter wheat cultivation technology is a long process. Productivity increases significantly on fertile soils in the presence of constant precipitation in the warm season, as well as in the absence of severe frosts.
Winter wheat cultivation technology is a long process. Productivity increases significantly on fertile soils in the presence of constant precipitation in the warm season, as well as in the absence of severe frosts.
Requirements for soil and climate conditions
 Wheat will give a good harvest on fertile soils, the acidity of which ranges from 6 to 7.5. Sufficiently moist chernozems or other types of soil that contain a large amount of nutrients are suitable for it. The amount of the harvest also depends on the relief. In low swampy areas, plants grow and develop poorly.
Wheat will give a good harvest on fertile soils, the acidity of which ranges from 6 to 7.5. Sufficiently moist chernozems or other types of soil that contain a large amount of nutrients are suitable for it. The amount of the harvest also depends on the relief. In low swampy areas, plants grow and develop poorly.
Modern varieties of winter wheat are highly frost-resistant. With a good layer of snow, these plants can withstand temperatures as low as -20-30 ° C. However, in the absence of snow, plants can die even at -15 ᴼС.
For such wheat, temperature fluctuations in spring are especially dangerous. If frosts have occurred after the vegetation processes have resumed, they can completely destroy the crop.
Fertilizers
 It is important to fertilize different varieties of winter wheat on time and correctly, otherwise the harvest will turn out to be poor. There are two main ways to apply fertilizers: root top dressing (in the ground) and foliar, or foliar. This crop can be fed several times, depending on the phase of its growing season:
It is important to fertilize different varieties of winter wheat on time and correctly, otherwise the harvest will turn out to be poor. There are two main ways to apply fertilizers: root top dressing (in the ground) and foliar, or foliar. This crop can be fed several times, depending on the phase of its growing season:
- during planting - potassium, phosphorus, organic fertilizers;
- nitrogen supplements - in the spring, as they are quickly washed out of the soil.
One of the main ways to improve the quality of your crop by adding fertilizer is foliar feeding.
Leaf top dressing of winter wheat in spring with urea allows you to get large heavy grains and increase their number. Unlike other ammonium fertilizers (ammonia water and nitrate), this substance does not burn plants.
Treatment for diseases and weeds
 During the germination period, wheat does not develop well if weeds interfere with it. Winter wheat herbicides are chemical solutions that fight weeds. Usually they are introduced into the soil in April and May, when the activity of unwanted plants increases. Some combine nitrogen fertilization with herbicide treatments.
During the germination period, wheat does not develop well if weeds interfere with it. Winter wheat herbicides are chemical solutions that fight weeds. Usually they are introduced into the soil in April and May, when the activity of unwanted plants increases. Some combine nitrogen fertilization with herbicide treatments.
Diseases of winter wheat are various bacterial lesions (black, yellow, basal bacteriosis), putrefactive processes in the roots, fungal lesions (fusarium) and others. For each disease there are special preparations that are introduced into the soil or sprayed with green mass.
Winter wheat is grown in temperate climates. It is a high-yielding crop whose grains and stems are used in the food industry and agriculture. However, the yield will not be high if you do not follow all the rules for growing wheat. It will grow well only on certain types of soil with a special fertilization and watering regime.