Symptoms of goat diseases and their treatment at home
 Domestic goats are the most unpretentious animals. Symptoms of goat disease and their treatment depend on the physical condition of the animals. The stronger the body, the easier the disease progresses, the more difficult it is to diagnose. However, the ailment missed in the acute stage turns into a chronic form and is waiting in the wings.
Domestic goats are the most unpretentious animals. Symptoms of goat disease and their treatment depend on the physical condition of the animals. The stronger the body, the easier the disease progresses, the more difficult it is to diagnose. However, the ailment missed in the acute stage turns into a chronic form and is waiting in the wings.
Varieties of diseases of the goat herd

- non-infectious;
- infectious;
- parasitic;
- blood parasitic diseases.
Often, the symptoms of goat disease are unclear, and treatment is prescribed by a specialist. In the case of a non-communicable disease, the animal is not separated from the herd; in other cases, measures are taken to prevent the spread of the disease.
Non-communicable diseases arise from improper feeding and maintenance. Goat the animal is restless, and often the desire to take the barrier ends in injury. Non-communicable diseases include inflammation associated with the common cold, especially in goats after lambing. If there is no bacterial or microbial process, the animal can be left in the herd.
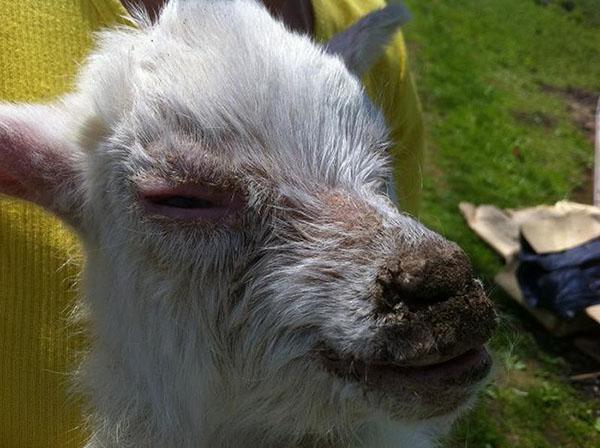 All diseases of a bacterial, viral, microbial nature are transmitted through shared utensils, feces, sniffing and milk. If these symptoms are present and the goat disease is treated with antibiotics, the animal should be isolated.
All diseases of a bacterial, viral, microbial nature are transmitted through shared utensils, feces, sniffing and milk. If these symptoms are present and the goat disease is treated with antibiotics, the animal should be isolated.
Parasitic diseases are associated with the development of foreign organisms in the organs of the animal, which feed on the flesh of the donor. The infection gets:
- while walking,
- through tick vectors,
- swallowing helminth formations with food and water.
There are many such diseases; parasites live in the blood, liver, stomach and other parts of the body. They eat living flesh, reproduce, and the goat gradually turns into a walking corpse. If a problem is detected, sanitization of the places where sick goats are kept and their treatment with special preparations.
Ticks and lice settle on the skin of animals, infect with a bunch of diseases, lead to scratching and constant excitement. The herd is subjected to repeated processing until all parasites are removed.
Diseases of lactating goats
 Any medical treatment, viruses and bacteria contained in the body, parasites that reproduce themselves, for a milking goat become a double danger. She is exhausted, fighting the disease, transmitting the infection with milk to a goat, a cat, and people. Therefore, by the lambing period, it is necessary to take all preventive measures.
Any medical treatment, viruses and bacteria contained in the body, parasites that reproduce themselves, for a milking goat become a double danger. She is exhausted, fighting the disease, transmitting the infection with milk to a goat, a cat, and people. Therefore, by the lambing period, it is necessary to take all preventive measures.
The goat from which we drink milk must be healthy. But it is the goat's strong immunity and patience, when there is no apparent reason to do tests, that introduces poison instead of a medicinal product.
Even before lambing, the hostess should make sure that she is launching a healthy goat. Stop milking the goat 4-6 weeks before lambing. A few days before the onset of childbirth, juicy feed is excluded, mixed feed is replaced with bran. The goat has been protected from colds and injuries for the last month. It will be difficult for an oily goat to lamb, so roughage is given, but not succulent.
 To prevent the udder from becoming coarse, even before giving birth, the surplus colostrum is removed and stored in the refrigerator in order to water the newborn kids. Diseases of goats after lambing are associated with ruptures, absent afterbirth or prolapse of the uterus.All these are studied consequences and with the help of a veterinarian everything is cured. The main thing is not to bring the infection inside at this time.
To prevent the udder from becoming coarse, even before giving birth, the surplus colostrum is removed and stored in the refrigerator in order to water the newborn kids. Diseases of goats after lambing are associated with ruptures, absent afterbirth or prolapse of the uterus.All these are studied consequences and with the help of a veterinarian everything is cured. The main thing is not to bring the infection inside at this time.
Lambing should be kept in a clean, dry area.
Postpartum infection occurs by the colonization of microbes in the birth canal. The temperature rises to 410 and the goat becomes lethargic. It is impossible not to treat - the animal will die.
Udder diseases
 Now think about untreated infections. A weakened animal with low immunity is their prey. It is at this moment that udder diseases begin in goats. It is easy to lose milk if the hygienic and climatic conditions of detention are not observed. Inflammation of the udder can be primary, and the infection will come from a dirty bedding or towel through open nipples.
Now think about untreated infections. A weakened animal with low immunity is their prey. It is at this moment that udder diseases begin in goats. It is easy to lose milk if the hygienic and climatic conditions of detention are not observed. Inflammation of the udder can be primary, and the infection will come from a dirty bedding or towel through open nipples.
A bump may appear on the goat's udder. This is the result of a staphylococcal infection that got through the hair follicles and caused an abscess. This is a very painful manifestation, similar to a human boil.
 If suppuration has begun, it is accelerated by applying ichthyol ointment, petroleum jelly with calendula. Broken open wounds are disinfected with iodine or alcohol. With a solution of penicillin, streptocide, the nucleus of the abscess is treated and the wound is healed, using medical and folk remedies.
If suppuration has begun, it is accelerated by applying ichthyol ointment, petroleum jelly with calendula. Broken open wounds are disinfected with iodine or alcohol. With a solution of penicillin, streptocide, the nucleus of the abscess is treated and the wound is healed, using medical and folk remedies.
Teat cracks occur during milking, when hygiene is poor and the skin becomes dry. Cracks will make themselves felt in blood.
Care, disinfection, lubrication with baby cream will correct the situation. A goat can damage the udder with horns if it itches. See if insects have started.
The milk-filled udder consists of delicate tissue that is easily injured by rough handling. The swollen udder is painful, blood may appear, the ailment by all signs resembles mastitis... Only light massage, compresses and warming ointments will save the day.
For all of these diseases, milk can be given to a goat, eaten if there is no foreign smell from the care products.
With mastitis, udder disease in goats, milk becomes unusable. Bacteria that cause inflammation develop in the milk ducts, and together with milk they can infect kids and humans.
Mastitis is distinguished:
- streptococcal;
- serous;
- gangrenous;
- catarrhal.
Regardless of the type of bacteria, they multiply rapidly in favorable conditions, and the appearance of blood, broaches, mucus, lumps that clog the milk ducts in the milk becomes visible signs of the disease.
 Folk remedies can alleviate the condition of the nurse, but specially selected antibiotics can kill the infection. To preserve the microflora of the stomach at this time, the doctor prescribes additional medications and vitamins.
Folk remedies can alleviate the condition of the nurse, but specially selected antibiotics can kill the infection. To preserve the microflora of the stomach at this time, the doctor prescribes additional medications and vitamins.
Hello, one part of the goat's udder has become almost empty. Tonight we milked separately and the milk is thick yellow, please tell me what is it with the goat?
See your local veterinarian. We have no right to give any recommendations without direct examination of the animal.