Types of nematodes and the fight against them in the garden
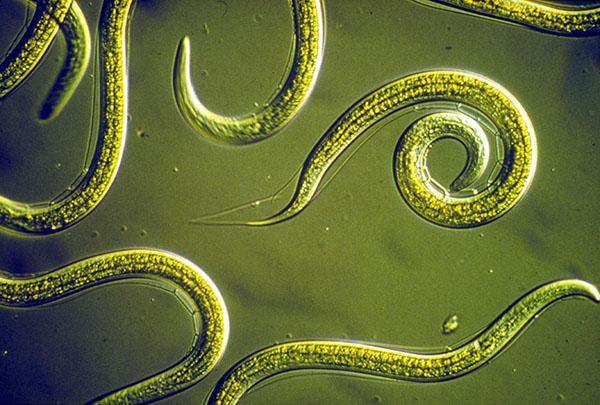 Different types of nematodes are adapted to a free or parasitic lifestyle. In total, there are more than 24 thousand of them - they can live in water and soil, as well as in humans and animals. These are small roundworms that cause hookworm disease. Free-living species cause difficulties for cultivation of cultivated plants, since they parasitize on their roots and aboveground parts. A set of measures has been developed to combat nematodes, which includes, among other things, the use of toxic drugs. To understand how to get rid of these pests, you need to figure out what nematodes are and what kind of species appeared on the site.
Different types of nematodes are adapted to a free or parasitic lifestyle. In total, there are more than 24 thousand of them - they can live in water and soil, as well as in humans and animals. These are small roundworms that cause hookworm disease. Free-living species cause difficulties for cultivation of cultivated plants, since they parasitize on their roots and aboveground parts. A set of measures has been developed to combat nematodes, which includes, among other things, the use of toxic drugs. To understand how to get rid of these pests, you need to figure out what nematodes are and what kind of species appeared on the site.
Nematode species
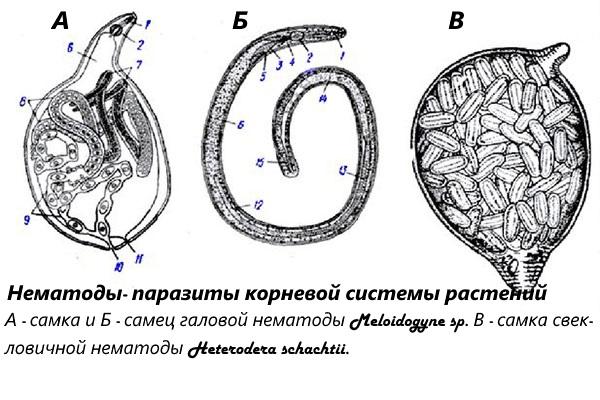
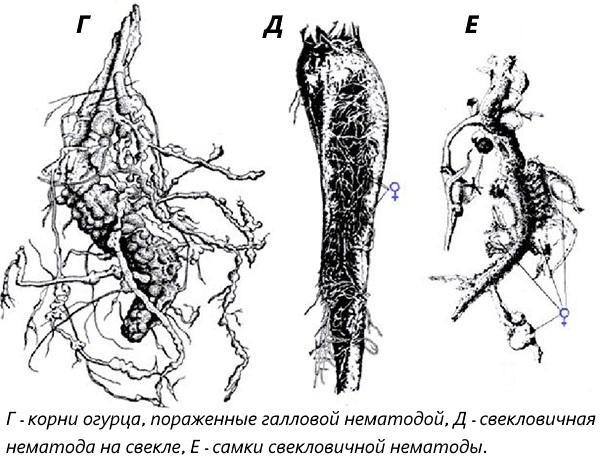
Most nematode species cannot migrate quickly, so their number at different corners of the same field or area may differ. However, treatments should be carried out around the entire perimeter of the site.
Leafy varieties
 A leaf nematode is a worm up to 1 mm in length. It moves relatively quickly and parasitizes on the green mass of flowers and garden crops. When they appear, spots appear on them, plants slow down in growth and development, bear poor fruit and can dry out completely. These species are frost-resistant and can hibernate in fallen leaves.
A leaf nematode is a worm up to 1 mm in length. It moves relatively quickly and parasitizes on the green mass of flowers and garden crops. When they appear, spots appear on them, plants slow down in growth and development, bear poor fruit and can dry out completely. These species are frost-resistant and can hibernate in fallen leaves.
Most often, those plants that are grown in greenhouses are affected by the leaf nematode.
It is useful for novice gardeners to know several features of leaf nematodes:
- most often they affect strawberries, chrysanthemums, nephrolepis;
- move quickly and can spread over large areas;
- reproduction of nematodes occurs within one leaf or plant, until its complete death.
The first sign of damage to a plant by leafy nematodes is the appearance of asymmetrical yellow spots on the leaves. Then they turn brown, and the leaf plate gradually becomes thinner, becoming like parchment. Over time, the leaves dry out and fall off, and the plant dies. If a nematode has appeared on a potted houseplant, it is easier to discard it along with the container it was in.
The use of chemicals against parasitic worms indoors can be hazardous to health.
Stem parasites
 Stem nematodes are small (up to 1.7 mm) filamentous worms that parasitize stems, leaves and buds. Their larvae enter the plant through the roots, and then continue to develop in the tissues of the green mass. They release toxins that are harmful to plants, due to which the growth of shoots stops. If the worms infect the buds, the flowering process stops. Crops on which stem nematodes parasitize have a characteristic appearance. Growths appear on their stems, and the growth of shoots is uneven. The bushes are deformed and die over time.
Stem nematodes are small (up to 1.7 mm) filamentous worms that parasitize stems, leaves and buds. Their larvae enter the plant through the roots, and then continue to develop in the tissues of the green mass. They release toxins that are harmful to plants, due to which the growth of shoots stops. If the worms infect the buds, the flowering process stops. Crops on which stem nematodes parasitize have a characteristic appearance. Growths appear on their stems, and the growth of shoots is uneven. The bushes are deformed and die over time.
The main way to combat nematodes in the garden is to properly prepare the soil and planting material.Diseased plants are often removed along with the root and burned so that the parasites do not spread to neighboring areas. Before sowing, the soil is treated with special agents that suppress the growth of worms. One of the methods how to get rid of nematodes in onions and bulbous ornamental plants, is warming up. The bulbs are removed from the soil and kept for 10-15 minutes in water heated to 45-50 degrees.
Stem nematodes are selective and only affect certain plant species. Most often they appear on hyacinths, violets, onions and garlic, parsley, tomatoes, radishes and cucumbers.
Root species
 Root nematodes are a dangerous pest because they can parasitize many plant species at the same time. They are small: males reach 2 mm in length, females are smaller (up to 1 mm), but wide. Pests are also called gall nematodes. They infect the roots of plants and form galls on them - characteristic growths that impede the flow of nutrients.
Root nematodes are a dangerous pest because they can parasitize many plant species at the same time. They are small: males reach 2 mm in length, females are smaller (up to 1 mm), but wide. Pests are also called gall nematodes. They infect the roots of plants and form galls on them - characteristic growths that impede the flow of nutrients.
Soil nematodes pose a danger to annual and perennial plants, garden crops, ornamental flowers, berry bushes and fruit trees. The life cycle of a pest can last from 19 to 45 days. Galls appearing on rhizomes are shelters for females, which can lay up to 2 thousand eggs in their entire life. The emerging larvae develop for some time in the roots and feed on plant juices. Then they transform into adults (males or females), and their life cycle repeats.
Measures to combat rootworm nematode are ineffective, since it is possible to notice its appearance and recognize the parasite only at later stages.
The general picture includes signs:
- slow growth, slow flowering and fruiting;
- on the roots - the appearance of characteristic thickenings (galls);
- symptoms of lack of water and nutrients, even on moist fertile soil.
Control measures for root nematode - prevention of its appearance. It is most dangerous for various types of succulents, including ornamental cacti. New plants are planted in separate containers, and a tool soaked in formalin or lysol is used to loosen the soil. Before planting new specimens in the ground, treat their rhizomes with solutions of parathion or fosdrin, and then rinse with clean water.
The simplest and most effective method of dealing with soil nematodes is the correct preparation of the soil for planting. It is recommended to bake it at a temperature of 100 ° for 2 hours. This procedure will completely clear the soil from nematodes, larvae of other pests and weeds, but is only suitable for potted plants. It is also worth remembering that the nematode slows down in development and gradually dies under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Houseplants, especially cacti, should be kept in well-lit areas as much as possible.
Potato nematode
 The potato nematode is a distinct type of roundworm. They parasitize the root system of the nightshade family, including potatoes and tomatoes. The shoots of such plants are weak, with a yellowish tinge, and quickly dry out. The appearance of a nematode reduces the yield of 50-80% or more - tubers grow small and unusable, and are absent on some bushes. In addition, the pest causes financial losses: the crop harvested in areas with an identified nematode is prohibited for transportation and sale. The plantings are closed for quarantine until the soil is completely cleaned.
The potato nematode is a distinct type of roundworm. They parasitize the root system of the nightshade family, including potatoes and tomatoes. The shoots of such plants are weak, with a yellowish tinge, and quickly dry out. The appearance of a nematode reduces the yield of 50-80% or more - tubers grow small and unusable, and are absent on some bushes. In addition, the pest causes financial losses: the crop harvested in areas with an identified nematode is prohibited for transportation and sale. The plantings are closed for quarantine until the soil is completely cleaned.
Drugs against nematodes
 On sale there are special remedies for nematodes - plant parasites. Nematicides are used on already infested areas as they are highly toxic and not suitable for routine preventive treatments.
On sale there are special remedies for nematodes - plant parasites. Nematicides are used on already infested areas as they are highly toxic and not suitable for routine preventive treatments.
There are two types of such drugs:
- fumigants;
- the rest (carbamate derivatives, phosphorus compounds);
- biologics.
Fumigants are toxic poisons that target nematodes through their respiratory system. These include chloropicrin, carbation, nemagon, methyl bromine. They are used by introducing them into the soil, as well as for processing seeds. Some of them, including chloropicrin, have a complex effect and completely disinfect the soil from nematodes, fungi and bacteria.
The rest of the drugs are available in liquid form. Some of them (methylmercaptophos, phosphamide, karbofos) have a contact effect and penetrate the skin of pests. Dimethoate and its analogs are systemic drugs that affect parasites after entering their digestive system. Such products are suitable for spraying green mass of plants from leaf nematodes.
A separate group of nematicides is biological products. They differ in composition, but all contain living components that adversely affect nematodes. These can be mushrooms that feed on worms, as well as plant extracts (garlic, tansy) or various waste products of microorganisms.
Nematodes can develop not only in soil or green parts of plants, but also in water bodies. One way to get rid of a nematode in a pool is to use a lot of hydrogen peroxide. It must be in contact with all surfaces that have come into contact with contaminated water.
Preventive actions
 It is difficult to deal with a nematode, so it is better to timely prevent its appearance. If the use of toxic chemicals is required to clean the soil from the parasite, then it can be prevented by simpler methods.
It is difficult to deal with a nematode, so it is better to timely prevent its appearance. If the use of toxic chemicals is required to clean the soil from the parasite, then it can be prevented by simpler methods.
Prevention of nematodes of plants includes the following measures:
- careful selection of seed - you can, among other things, pay attention to varieties that show high resistance to nematodes;
- warming tubers and bulbs before planting in the ground;
- placing some varieties of plants in the aisles that adversely affect the development of nematodes (calendula, marigolds);
- timely removal of affected plants with their subsequent burning.
Nematodes in soil and control of them is a huge problem. These pests cannot be seen with the naked eye, especially those that parasitize the rhizome. For this reason, their appearance becomes noticeable only when the plants have already been irreparably damaged. In most cases, it is recommended to burn the affected specimens and then disinfect the soil for new plantings. Preventive treatment of soil and planting material is of great importance.