Growing and caring for grapes on a personal plot
 Grapes grown over millennia have undergone major changes over the past couple of centuries. Many new varieties have appeared that regularly yield crops even in those regions where they had never heard of the wine berry before. Breeders have bred not only winter-hardy varieties, but also species that are little affected by diseases that are dangerous for the culture, giving extra-large brushes and incredibly tasty berries, completely devoid of seeds. And yet, growers know that you can get a decent return on a bush of even the most productive and unpretentious variety by investing in cultivation and care for grapes a lot of work and skill.
Grapes grown over millennia have undergone major changes over the past couple of centuries. Many new varieties have appeared that regularly yield crops even in those regions where they had never heard of the wine berry before. Breeders have bred not only winter-hardy varieties, but also species that are little affected by diseases that are dangerous for the culture, giving extra-large brushes and incredibly tasty berries, completely devoid of seeds. And yet, growers know that you can get a decent return on a bush of even the most productive and unpretentious variety by investing in cultivation and care for grapes a lot of work and skill.
The first, after planting seedlings in the ground, a contribution to the future harvest is the formation of a grape bush, which begins from the first year of the plant's life and, together with the shape of the plant's crown, determines its fruiting.
With a competent approach, by the fourth year the bush takes on its final appearance, but this does not mean that the work of the grower is completed.
On this topic:preparing grapes for winter video.
Formation of a grape bush

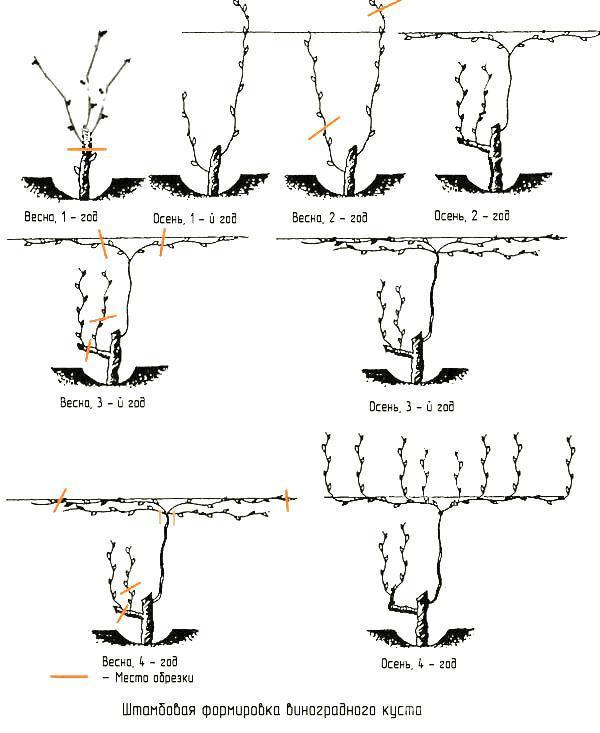 The result of the correct formation of the grape bush is:
The result of the correct formation of the grape bush is:
- regular and, in accordance with varietal characteristics, bountiful harvest;
- quality growth at the end of the growing season;
- a plant that tolerates winter without problems and does not suffer from diseases of grapes and its pests common in the area;
- providing a simple care for a grape seedling;
- facilitating vine pruning and watering, rejuvenating and adjusting the existing load.
When wondering how to grow grapes, some novice gardeners act on a whim, not paying pruning a bush due attention. However, there are many well-established options and types of forms that allow you to get good results in a wide variety of farming conditions. With the help of spring pruning, a grape bush is formed with or without a stem of various heights.
Most often, growers give rooting grape seedlings:
- capitate shape without perennial sleeves, but with a thickened upper part of the trunk, from which, thanks to pruning grapes a mass of new shoots grows on 1–2 eyes or on a ring;
- cup-shaped with sleeves of various lengths extending from the trunk, resting on stakes;
- a form with fruit links directed in one or two directions, the entire growth on which is distributed on a vertical trellis;
- cordon form with one or more perennial cordons, along which fruit links or branches are distributed. This option is convenient in growing and caring for grapes, gives high yields, but is more common in regions with a warm climate, where the vine does not require shelter for the winter;
- fan-shaped and half-fan shaped, resting on a trellis and having several sleeves of different lengths and strengths.
It is the various variants and combinations of fans that have received the greatest recognition of winegrowers in Russia, since such a grape bush is easy to care for.
 The bush can be adjusted if desired, and when arranging the trellis, the plants receive enough air, light and nutrition, give consistently high yields, can be removed and sheltered for the winter. The main part of the work on the formation of a grape bush is carried out in the spring, in the summer, excess and overgrowing shoots and stepsons break off, a garter and other procedures are carried out, aimed at maintaining fruiting and the intended shape of the plant.
The bush can be adjusted if desired, and when arranging the trellis, the plants receive enough air, light and nutrition, give consistently high yields, can be removed and sheltered for the winter. The main part of the work on the formation of a grape bush is carried out in the spring, in the summer, excess and overgrowing shoots and stepsons break off, a garter and other procedures are carried out, aimed at maintaining fruiting and the intended shape of the plant.
Tapestry for grapes
 Since grapes are a vigorous liana, in most cases reliable and comfortable support is needed to grow them and facilitate maintenance. The presence of such structures is especially important in case of a stemless crown shape and the cultivation of vigorous varieties, as well as when using grapes for planting canopies, gazebos and other buildings.
Since grapes are a vigorous liana, in most cases reliable and comfortable support is needed to grow them and facilitate maintenance. The presence of such structures is especially important in case of a stemless crown shape and the cultivation of vigorous varieties, as well as when using grapes for planting canopies, gazebos and other buildings.
Walls, poles, stakes and even trees growing next to bushes can serve as a support for the vine, but the best solution would be to install a special trellis for grapes.
 In amateur gardening, two types of construction are most common:
In amateur gardening, two types of construction are most common:
- vertical trellis, where grape shoots are located in one plane;
- an inclined trellis, on which the shoots are spaced into two planes at an angle to each other.
 In both cases, reliable pillars serve as the support of the structure; rows of strong wire are pulled between them, which will have to withstand not only the weight of the shoots, but also the weight of the pouring brushes. A single-plane trellis for grapes is simpler in the device and much cheaper, but to obtain high yields from a bush, a two-plane option is more convenient, providing a large area to support fruiting shoots and withstanding a serious weight of the vine.
In both cases, reliable pillars serve as the support of the structure; rows of strong wire are pulled between them, which will have to withstand not only the weight of the shoots, but also the weight of the pouring brushes. A single-plane trellis for grapes is simpler in the device and much cheaper, but to obtain high yields from a bush, a two-plane option is more convenient, providing a large area to support fruiting shoots and withstanding a serious weight of the vine.
To simplify the cultivation and care of grapes, between the trellises, there are aisles sufficient to remove the bushes and cover them during the cold weather, as well as to provide sufficient lighting for the plantings, and the rows did not overlap. It is better if the grape trellis on the site is located from north to south. In this case, the height of the structure is chosen depending on the growth of the grower, the characteristics of the variety and the chosen shape of the bush.
How to tie grapes
 As the grapes grow during the growing season, the shoots are tied several times to the horizontal rows of the trellis or fixed on other types of supports. In this case, the garter, during which the shoots are evenly distributed in one or two planes, serves to solve several problems:
As the grapes grow during the growing season, the shoots are tied several times to the horizontal rows of the trellis or fixed on other types of supports. In this case, the garter, during which the shoots are evenly distributed in one or two planes, serves to solve several problems:
- The plant is provided with the best light and air conditions.
- It is easier to trim and normalize the green mass and ovary.
- Carrying out foliar dressing of grapes, as well as performing "green pruning" is facilitated.
- Vertical shoots grow and mature better.
- The risk of developing grape disease and pest damage is reduced.
- The budding wine grower should know when and how to tie the grapes.
The first time to fix the position of the shoots is necessary when they are about 40-50 cm long and reach the bottom row on the trellis. Then, as they grow, the stems are tied sequentially to all rows.
As a garter, it is better to take scraps of textiles or knitwear, natural twine or twine, that is, means that do not compress or pinch the growing shoots. It is convenient to use a special tool for tying a grape seedling, which freely fixes the shoots with a plastic clip. On trellises, where the wire is stretched in two parallel rows, the shoots only start in such an interval, and the resulting whiskers are firmly fixed on the support over time. If the grapes grown on a gazebo or canopy are being taken care of, where free growth is provided, then such shoots do not need to be tied up.
Grape picking
 In the summer months, growing and caring for grapes does not involve pruning perennial shoots, but you cannot do without removing some of the green parts of the plant. Depending on the grape variety, the load experienced by the bush, as well as the cultivation conditions, plants from the buds on the shoots of the current year can produce a significant number of second-order shoots. If left unchecked, these stepchildren will take away much-needed nutrients from the future harvest and shade the entire bush. Excessive bush density is a serious risk factor for the development of grape diseases such as mildew and powdery mildew. Therefore, you should not wait for the growth of parasitic shoots.
In the summer months, growing and caring for grapes does not involve pruning perennial shoots, but you cannot do without removing some of the green parts of the plant. Depending on the grape variety, the load experienced by the bush, as well as the cultivation conditions, plants from the buds on the shoots of the current year can produce a significant number of second-order shoots. If left unchecked, these stepchildren will take away much-needed nutrients from the future harvest and shade the entire bush. Excessive bush density is a serious risk factor for the development of grape diseases such as mildew and powdery mildew. Therefore, you should not wait for the growth of parasitic shoots.
If in regions with short summer grape pinching consists in completely removing shoots already at the initial stages of development, then in the south, especially when growing early varieties, stepchildren are only shortened in order to get an additional harvest of sweet berries by autumn.
And in some cases, for example, when the vine suffers from frost or hail, grapes are not pinched at all. Stepsons replace the lack of green mass on the bush and help to resume the development of the bush.
Preventive treatment and foliar feeding of grapes
 Getting a high-quality and stable grape harvest is impossible without providing the plant with the proper amount of nutrients. Trellis cultivation gives the gardener the opportunity to use foliar dressing of grapes, an effective source of additional nutrition and minerals.
Getting a high-quality and stable grape harvest is impossible without providing the plant with the proper amount of nutrients. Trellis cultivation gives the gardener the opportunity to use foliar dressing of grapes, an effective source of additional nutrition and minerals.
The greatest need for such dressings is for grape bushes:
- before and after flowering;
- during the period when the coloring of berries begins;
- a few days before harvest.
For feeding grape seedlings and adult bushes, use a solution with a content of 5% superphosphate, 0.5% ammonium sulfate and 1% potassium salts. When the berries begin to ripen, the vine no longer needs nitrogen, but microelements such as zinc and boron can be added to the top dressing.
After flowering, the bushes are treated with a 1% solution of boric acid in combination with a fungicide that prevents the development of downy mildew, a disease that occurs in conditions of high humidity and has a detrimental effect not only on the future harvest, but on the entire grape plant. The final foliar dressing of grapes can be carried out on the basis of the infusion of wood ash. The introduction of such dressings, as well as spraying the bushes with fungicides and insecticides, is carried out in the second half of the day, when the temperature drops, the sun cannot burn the leaves and inflorescences or in cloudy weather. The longer the drops of the product remain on the greens, the greater the effect of the procedure.
How to treat grapes after rains, when fungicides and solutions of trace elements are washed off?
In the case of severe rainfall, the treatment is repeated as soon as possible, paying attention to spraying the bushes with Ridomil, especially during the period when the flowering has already been completed and the likelihood of mildew development is high.
 No less dangerous disease for grapes is powdery mildew, which often develops in dry hot weather. The first preventive treatment against this disease is carried out in the spring. If a light white fluff is found on the shoots, foliage and berries, at the initial stage, the treatment of grapes with soda and potassium permanganate in the form of a slightly pink solution will become a rather effective remedy for powdery mildew.
No less dangerous disease for grapes is powdery mildew, which often develops in dry hot weather. The first preventive treatment against this disease is carried out in the spring. If a light white fluff is found on the shoots, foliage and berries, at the initial stage, the treatment of grapes with soda and potassium permanganate in the form of a slightly pink solution will become a rather effective remedy for powdery mildew.
At the same time, do not forget that the effectiveness of dressings and remedies is really high if all the rules for growing and caring for grapes are fulfilled, weeds and extra shoots are removed in time, air and food are provided to all shoots.